Debugging a Container App with VS Code Docker extension
The VS Code Docker extension makes it easy to build, manage, debug and deploy containerized applications in Visual Studio Code.
Steps to debug a sample application running within a container
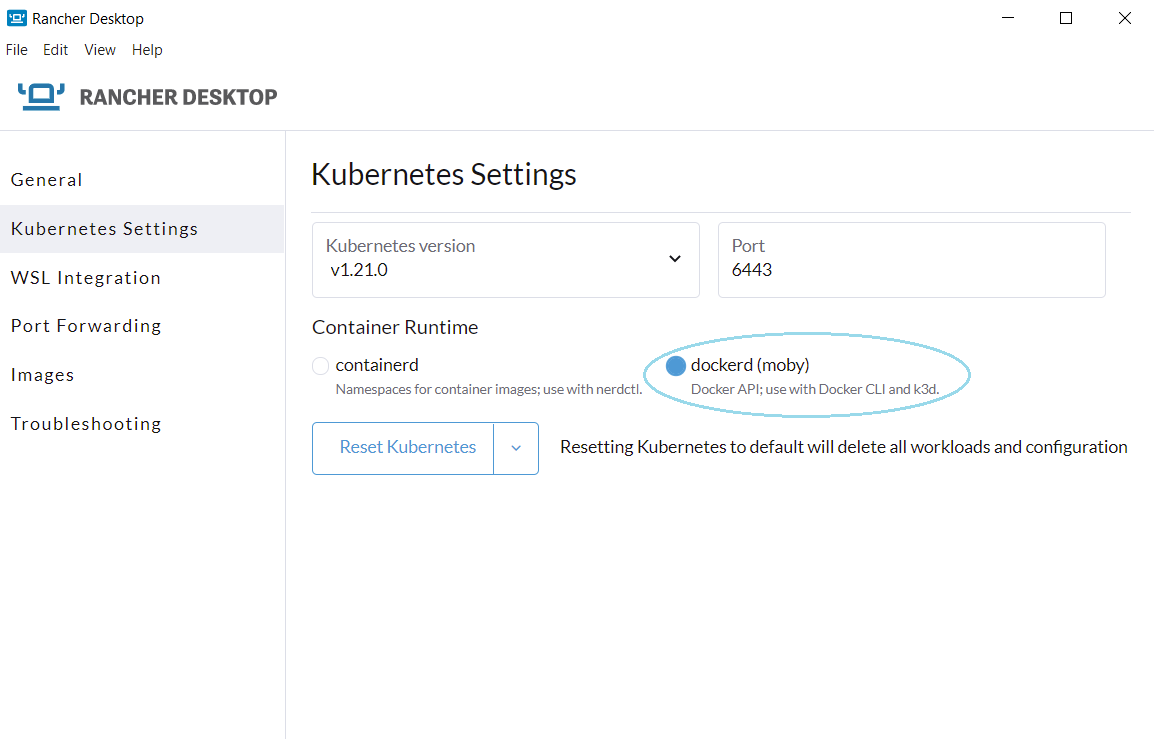
- Install and launch Rancher Desktop. Select
dockerd (moby)as the Container Runtime from theKubernetes Settingsmenu.
- Install and launch Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio Code Insiders. This tutorial uses Visual Studio Code.
- Install the VS Code Docker extension from the marketplace.
-
You can use the samples provided at this Github repository, https://github.com/bwateratmsft/samples. Clone this repository and open
expressappfolder in your VS Code session. -
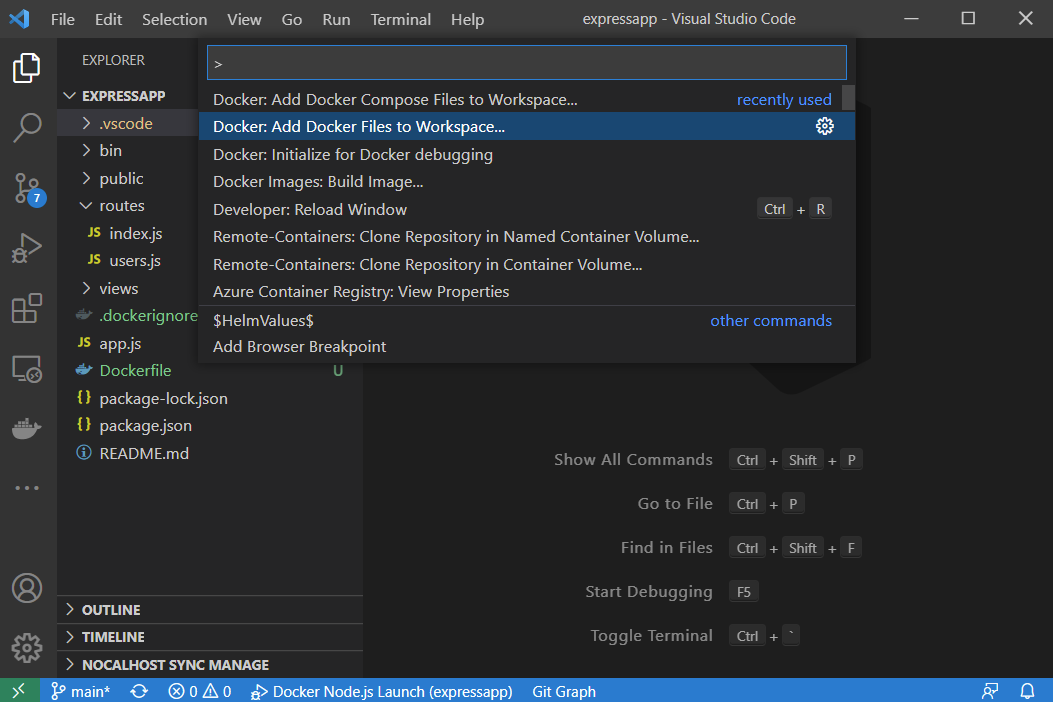
Open the command palette (Ctrl+Shift+P, F1, or Cmd+Shift+P) and run "Add Docker Files to Workspace". Since this is an Express app, Select
Node.jsas the Application Platform and3000(or any other available port) as theport. As it's a simple example, selectNofor theInclude optional Docker Compose filesprompt. This step adds aDockerfileandLaunch Configurationrequired to debug the application.
- Insert a breakpoint in the code.
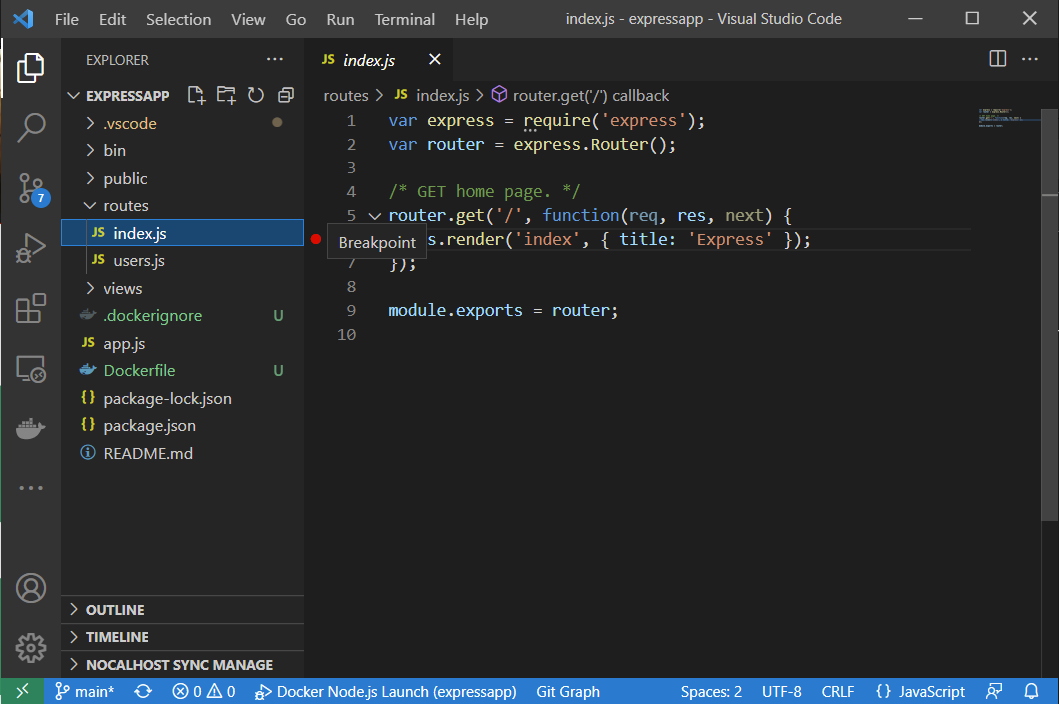
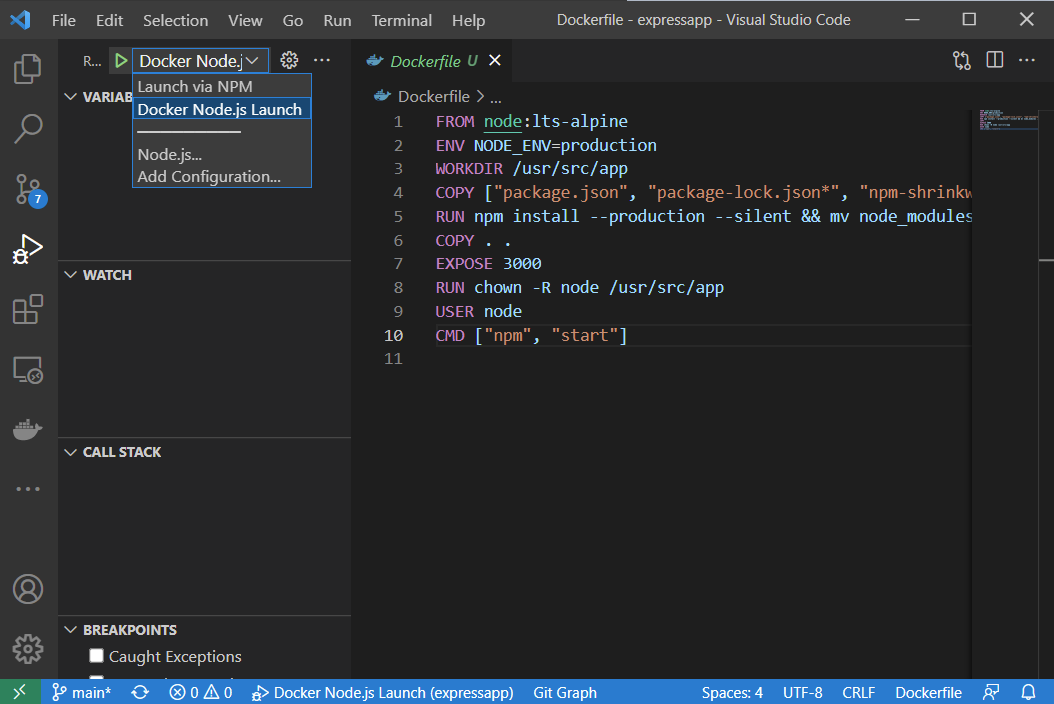
- In the Debug window at the top, switch the active debug configuration to "Docker Node.js Launch". Press
F5to start the application container inDebugmode. You will see the sample application's landing page opening in your browser, and the code execution stopping at the breakpoint. From here, you can debug the application as if it's running on your host.
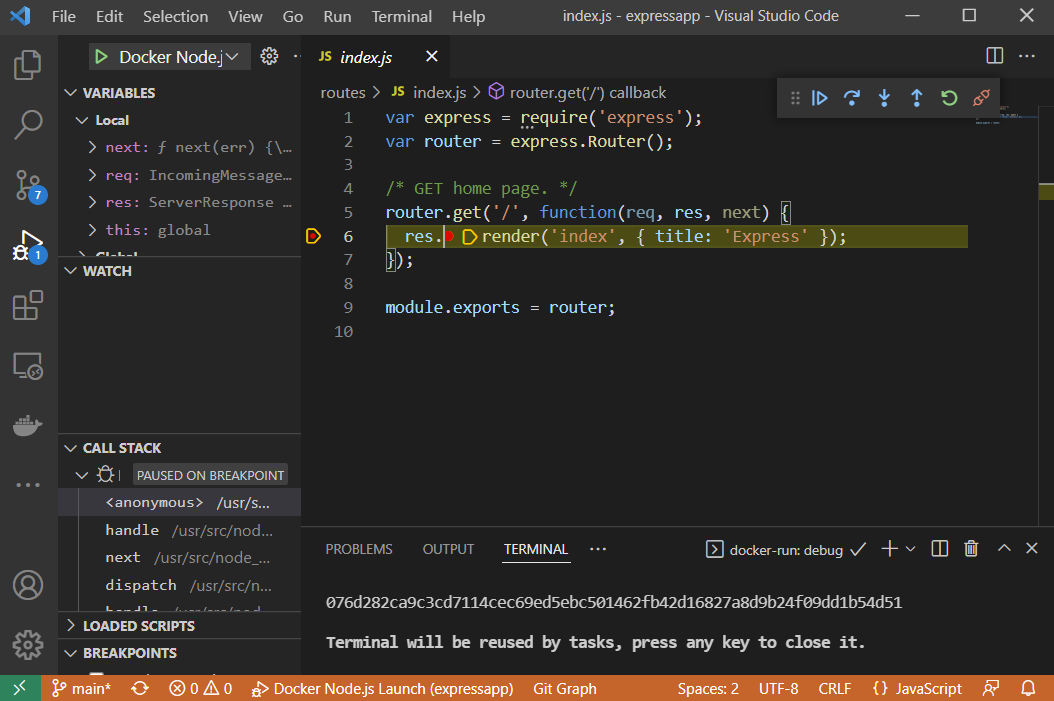
-
Sometimes, the application might not break at the set breakpoint on the first run as the debugging process may not have started. In this case, refresh the browser to trigger the execution again to hit the breakpoint. You can also get around this behavior by setting the property
inspectMode: 'break'intask.jsonfile to prevent the app from running until the debugger attaches. -
On some machines, the firewall settings might prevent the debugging process from establishing a connection between the host and the container processes. In this case, you can add a firewall rule to allow communication between the VM where the container is running and the host where you have the VS Code session running. On Windows, you can add a firewall rule by running the below command from a privileged powershell:
New-NetFirewallRule -Action Allow -Description 'Allow communication from WSL containers' -Direction Inbound -Enabled True -InterfaceAlias 'vEthernet (WSL)' -Name 'WSL Inbound' -DisplayName 'WSL Inbound'